Bold Is... unapologetic optimism for the future
Researchers at UT San Antonio are redefining what's possible in AI while keeping human well-being and safety front and center. From developing trustworthy AI that aids in natural disaster recovery to leveraging AI to improve trauma care and patient outcomes, UT San Antonio researchers are building a world where AI enhances our lives and society.

AI-powered communities bring new challenges and opportunities for the well-being of humans. In San Antonio, the MATRIX AI Consortium for Human Well-Being (MATRIX) leads AI research with a dedicated team of 87 scientists who share a common vision to solve the most pressing problems in AI through collaborations across academia, government, industry and healthcare ecosystems. MATRIX research focuses on four key areas: augmenting human capabilities; machine learning and deployment; neuro-inspired AI; and trustworthy AI.
Training the next generation of AI leaders
By training students in emerging fields, UT San Antonio promotes a growing and competitive workforce that maintains US technological leadership.

UT San Antonio is creating a new, first-of-its-kind college that integrates AI, cybersecurity, computing, data science and related disciplines. Located in San Antonio’s downtown tech corridor, the new college will drive innovation across industries through world-class academic programs, transdisciplinary research and strategic industry and community partnerships — all while propelling workforce development and economic growth in San Antonio, Texas and the nation.

AI is already shaping the medical field in the form of customized patient treatment plans, robotic surgeries, drug dosage and more. That’s why UT Health San Antonio and UT San Antonio have launched the first program in the United States to combine medicine and artificial intelligence. The five-year M.D/M.S. program enables physicians trained in San Antonio to uniquely lead in the practical use of AI to improve diagnostic and treatment outcomes. Additionally, UT Health San Antonio and UT San Antonio have several research programs underway to improve health care diagnostics and treatment with the help of AI.
Early Adopters of Generative AI in the Classroom
UT San Antonio faculty are embracing change and guiding students to explore the potential of generative AI in their research and coursework.
Bold Is... LEADING THE CHARGE OF CHANGE
Meet Dr. Dhireesha Kudithipudi
Dr. Kudithipudi, founder of the MATRIX AI Consortium, is a trailblazer in neuro-inspired AI, designing systems that mimic biological intelligence. She compassionately leads large multidisciplinary AI teams, including hundreds of scientists, with transparency and adaptability, fostering a culture of innovation. She initiated the country's first MD/MS program in AI and heads national centers of excellence focused on human well-being and energy-efficient AI. As a first-generation student and the first PhD graduate of Klesse College, Dr. Kudithipudi is paving the way for others to succeed and thrive.

AI Breakthroughs Transforming Human Health and Well-Being
UT San Antonio researchers are transforming health care with novel AI-powered solutions, improving patient outcomes and building a more accessible, efficient health care system.

Optimizing Trauma Care Using AI
Researchers in MATRIX, UT Health San Antonio and UT Tyler are collaborating on a newly funded project to develop and apply AI tools to the field of trauma care. The $1 million grant was awarded by the Trauma Research and Combat Casualty Care Collaborative (TRC4), an initiative of The University of Texas System. The research team will develop and deploy AI tools to improve trauma care decision-making among clinicians. The AI tools will also identify geographic hotspots where trauma care is frequently delayed. The data will help empower clinicians and administrators to improve and expedite trauma care.
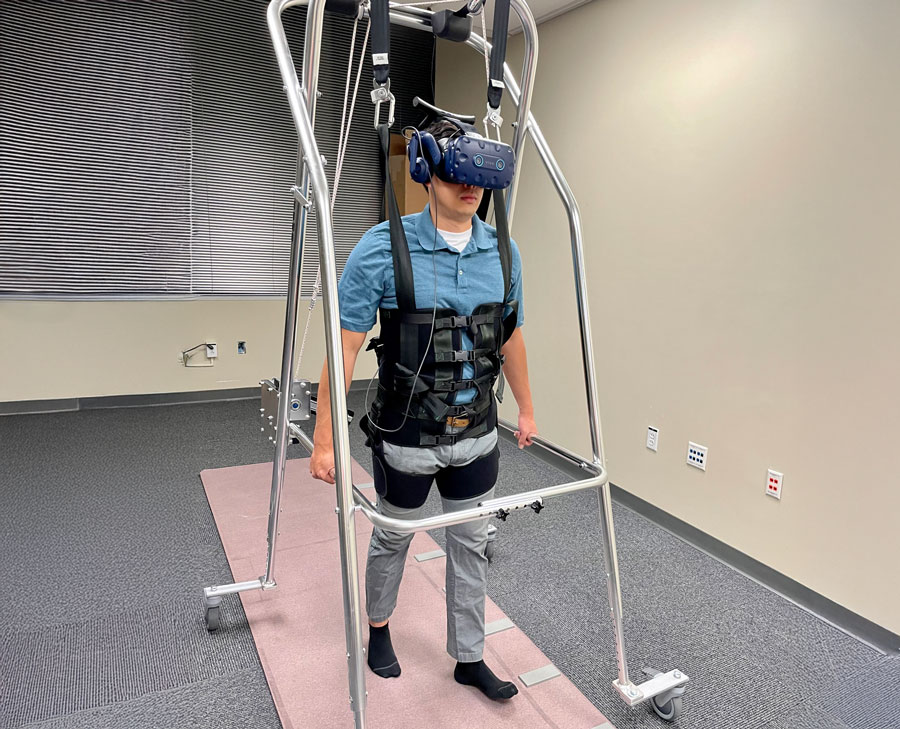
Balancing VR with AI: Making VR Accessible
Drs. John Quarles, Kevin Desai and Alberto Cordova are leading efforts to make virtual reality (VR) accessible for individuals with balance issues, such as the elderly and those with conditions like multiple sclerosis or Parkinson's, ultimately enhancing their quality of life. These individuals often miss out on VR's benefits, including education, fitness and entertainment, due to balance problems. By developing specialized audio feedback and using AI to predict and improve balance in real-time, the team is creating technology for real-world VR environments typically used at home, making VR more accessible and beneficial.
Responsible and Energy-Efficient Solutions
By advancing AI through resource and energy-efficient technologies, UT San Antonio is laying the foundation for AI systems that promote continual advancements in energy efficiency.

The newly-formed NSF ExpandAI Institute, NAIAD, is pioneering the future of AI by developing groundbreaking AI foundation models inspired by neural mechanisms and designing energy-efficient neuromorphic computing. The project aims to revolutionize edge computing and advance neuro-inspired edge platforms to address real-world challenges. NAIAD will work closely with researchers at NSF AI Institute ATHENA at Duke University in immersive research programs and strategic partnerships. NAIAD is committed to fostering a skilled AI workforce with 28 graduate fellows mentored by 10 faculty members and creating a vibrant community by bringing hundreds of individuals through annual AI Spring School and ExpandAI Leadership (EXAIL) workshops. NAIAD strengthens America's position in global science and technology leadership.

UT San Antonio was one of 15 universities to receive a grant to improve natural disaster resilience. UT San Antonio researchers Ao Du and Jiannan Cai received $400,000 in funding to develop AI technology that helps prioritize infrastructure repairs after devastating earthquakes. This promising approach aims to accelerate recovery efforts and minimize the impact of future disasters. By leveraging AI, decision-makers can quickly assess damage, allocate resources efficiently and expedite the restoration of critical transportation networks.
Tech Wonders: Open-Source AI for Everyone
UT San Antonio is pioneering the development of cutting-edge AI infrastructure that is accessible nationwide by providing the essential tools and computer systems needed to ensure AI functions effectively.

Leading the Largest Neuromorphic AI Computing Hub in the U.S.
UT San Antonio recently received $4 million from the National Science Foundation to lead The Neuromorphic Commons (THOR) to establish a specialized computing system that is the first of its kind in the United States. This initiative will create a new and unparalleled large-scale neuromorphic computing resource, working in close collaboration with leading AI industries and university partners such as UC San Diego, University of Tennessee, Knoxville and Harvard University. THOR will provide community researchers with open access to quickly test ideas, as well as a flexible option for conducting various AI and high-performance computing experiments to solve complex problems on the fly using relatively little energy.
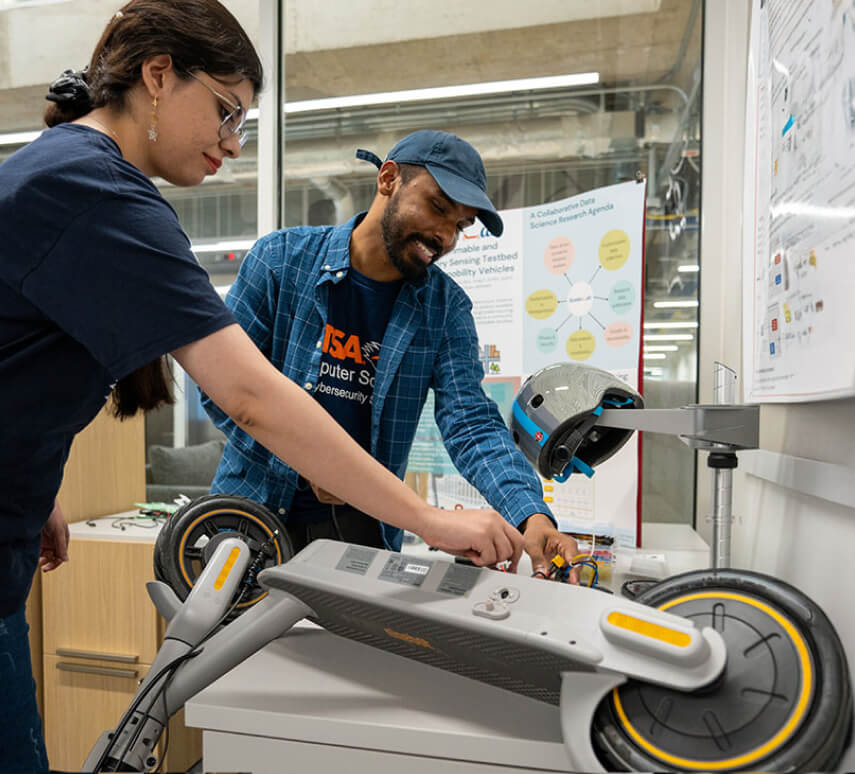

AI-Driven Mobility Solutions for Smart, Connected Cities
ScooterLab is a unique e-mobility infrastructure hosted by MATRIX at UT San Antonio, funded by a $1.9 million award from the National Science Foundation (NSF). This infrastructure consists of a fleet of e-scooters equipped with sensors to collect data while UT San Antonio students ride them around San Antonio. The data will enable multi-disciplinary research to advance pedestrian and rider safety, urban planning and energy efficiency in transportation. ScooterLab uses AI models to analyze the data, enhancing the performance and safety of the e-scooters and ensuring user privacy. The project's first deployment is already in motion, providing students with a convenient transportation option free of charge.
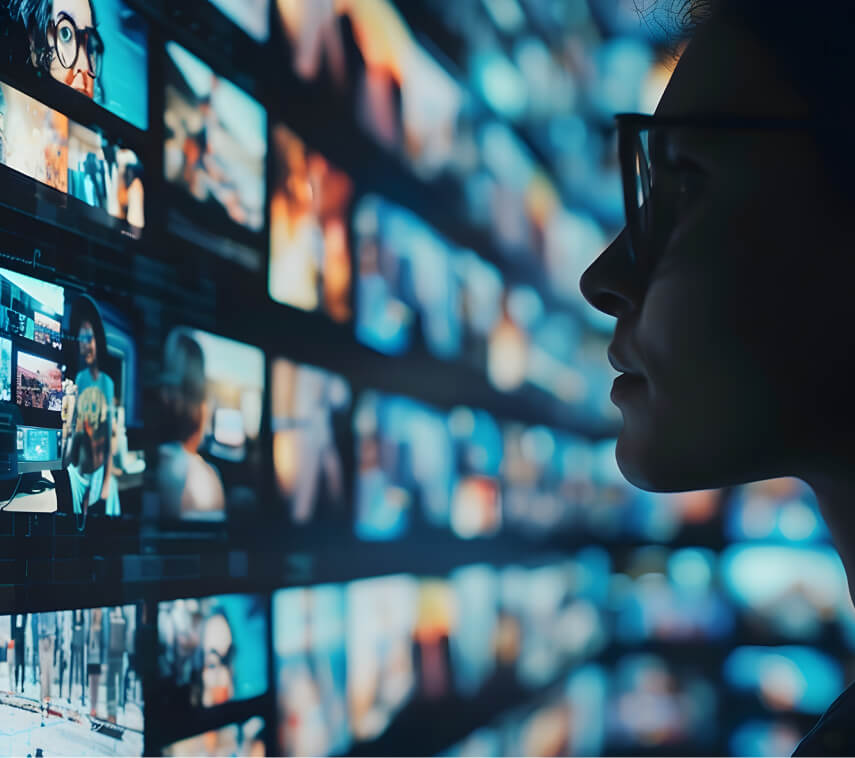

Making AI Image Recognition More Trustworthy
Artificial intelligence can help people process and comprehend large amounts of data with precision, but the modern image recognition platforms and computer vision models that are built into AI frequently overlook an important back-end feature called the alpha channel, which controls the transparency of images.
Researchers at UT San Antonio developed a proprietary attack simulator called AlphaDog to study how hackers can exploit this oversight. The vulnerabilities they uncovered could have important ramifications for autonomous vehicles reading road signs and software interpreting X-rays, MRIs and CT scans.
Bold Is... PIONEERING AI IN HEALTH CARE
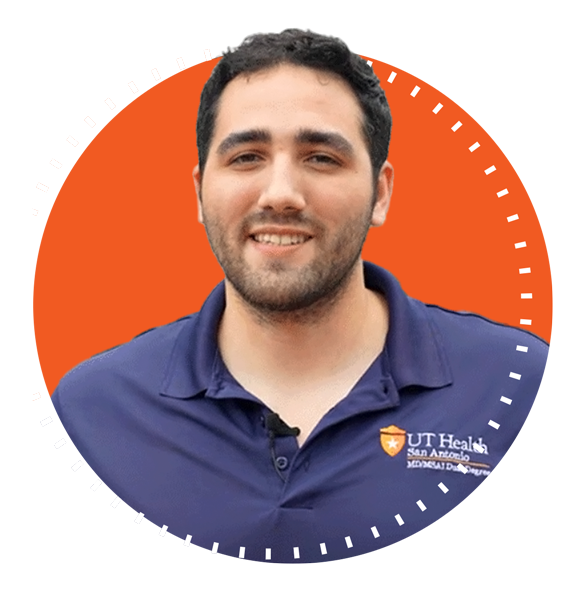
Meet Aaron Fanous, one of the first M.D./M.S. in AI grads
Aaron Fanous was among the first students to graduate with the dual Doctor of Medicine and Master of Science in Artificial Intelligence (M.D./M.S. in AI), making him one of a select group of doctors in the country with a specialization in artificial intelligence. During his studies, Fanous successfully applied AI to several functions in the medical field, including training a skin lesion identification model, which could improve diagnostic accuracy and save doctors countless hours.


Understanding Artificial Intelligence
A collaboration between Dr. Chien-jen Chiang and UT San Antonio Libraries Community-Engaged Digital Scholarship Hub, is focused on assessing the engagement and understanding of AI. This project involves surveying the UT San Antonio population over general AI literacy. Their responses will guide the development of a workshop to help develop and/or build upon their knowledge of AI tools as well as their understanding of ethics and accountability. This survey model will then be extended beyond the UT San Antonio community and into the larger San Antonio market in a second phase of the project.